Antifungals: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your skin itches, your nails thicken, or you get recurring yeast infections, you’re likely dealing with a fungus, a type of microorganism that thrives in warm, moist areas and can cause persistent infections. Also known as yeast or mold, these organisms aren’t bacteria—they need different tools to fight them. That’s where antifungals, medications designed specifically to kill or slow down fungal growth come in. Unlike antibiotics, which target bacteria, antifungals are built to handle fungi without wrecking your good bacteria.
Antifungals come in many forms: creams for athlete’s foot, pills for nail infections, sprays for ringworm, and even vaginal suppositories for yeast. Some are over-the-counter, others need a prescription. The most common ones include fluconazole, an oral antifungal often used for yeast infections, terbinafine, a go-to for stubborn nail fungus, and clotrimazole, a topical treatment found in most drugstore aisles. These aren’t just band-aids—they target the root of the problem. But they’re not harmless either. Some can mess with your liver, cause stomach upset, or interact with other meds you’re taking. That’s why knowing which one you need—and when to stop—is just as important as starting it.
Antifungals aren’t just for skin deep problems. They’re used in hospitals to treat serious systemic infections in people with weak immune systems. Even then, misuse can lead to drug-resistant strains. You wouldn’t take an antibiotic for a cold, and you shouldn’t use an antifungal for a rash that isn’t fungal. Misdiagnosing a skin issue as a yeast infection and slathering on cream for weeks? That can make things worse. The posts below cover real cases: how antifungals help with recurring yeast infections, why some people get side effects from long-term use, what happens when they don’t work, and how to tell if your rash is actually something else. You’ll find comparisons between common drugs, tips to avoid resistance, and warnings about what to watch for when your body doesn’t respond like it should. This isn’t just a list of meds—it’s a practical guide to using antifungals safely and effectively.
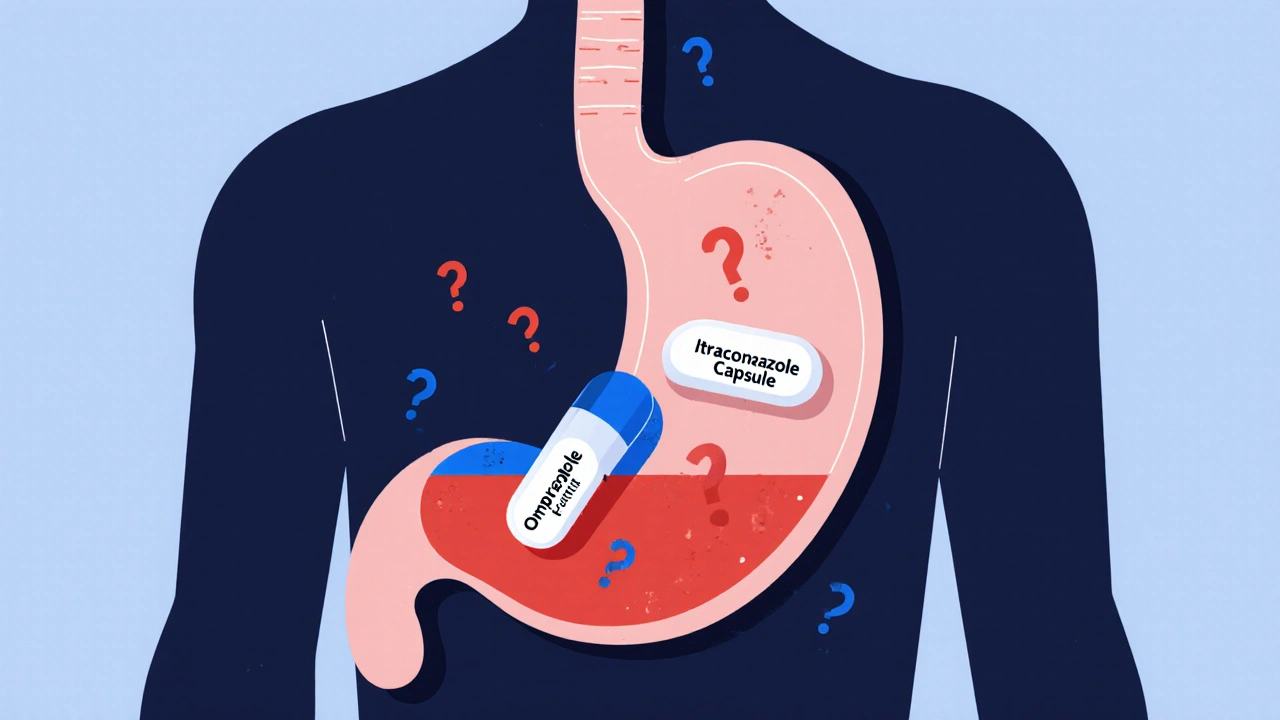
Proton Pump Inhibitors and Antifungals: How They Interfere with Absorption
Proton pump inhibitors can block the absorption of key antifungals like itraconazole, leading to treatment failure. Learn which drugs interact, how to fix it, and what new options are available.
View More




