Arrhythmia: Causes, Risks, and Medications That Affect Your Heart Rhythm
When your heart doesn’t beat in a steady rhythm, you’re dealing with arrhythmia, an abnormal heart rhythm that can feel like fluttering, pounding, or skipping beats. Also known as cardiac arrhythmia, it’s not always dangerous—but when it’s caused or worsened by medications, it can be life-threatening. Many people don’t realize that common drugs—like antidepressants, antibiotics, or even over-the-counter cold meds—can throw off your heart’s electrical system. You might feel fine until your pulse suddenly races or stumbles, and by then, it’s too late to ignore.
Medication interactions, how drugs interfere with each other’s effects on the body are a silent driver of arrhythmia. For example, taking an antifungal like itraconazole with a proton pump inhibitor can change how your body processes both, increasing the risk of irregular beats. Even something as simple as combining a diuretic with a muscle relaxant can drain your electrolytes—potassium and magnesium—leaving your heart vulnerable. The same goes for antidepressants like trazodone or amitriptyline, which are great for sleep or nerve pain but can slow or speed up your heart rhythm if you’re not monitored. And if you’re on opioids, antiemetics, or even NSAIDs for pain, those can quietly raise your risk, especially if you already have heart disease or are older.
Drug-induced arrhythmia, a type of irregular heartbeat triggered by medications is often missed because it looks like stress, fatigue, or caffeine. But if you’ve started a new pill and noticed your chest feels off—fluttering, dizzy, short of breath—it’s not just in your head. The posts below cover exactly these hidden connections: how antibiotics, antifungals, diuretics, and even sleep aids can trigger or worsen arrhythmia. You’ll find real-world examples of what to watch for, which meds to question with your doctor, and how to protect your heart without stopping essential treatments. No fluff. No guesses. Just what you need to know before your next prescription.
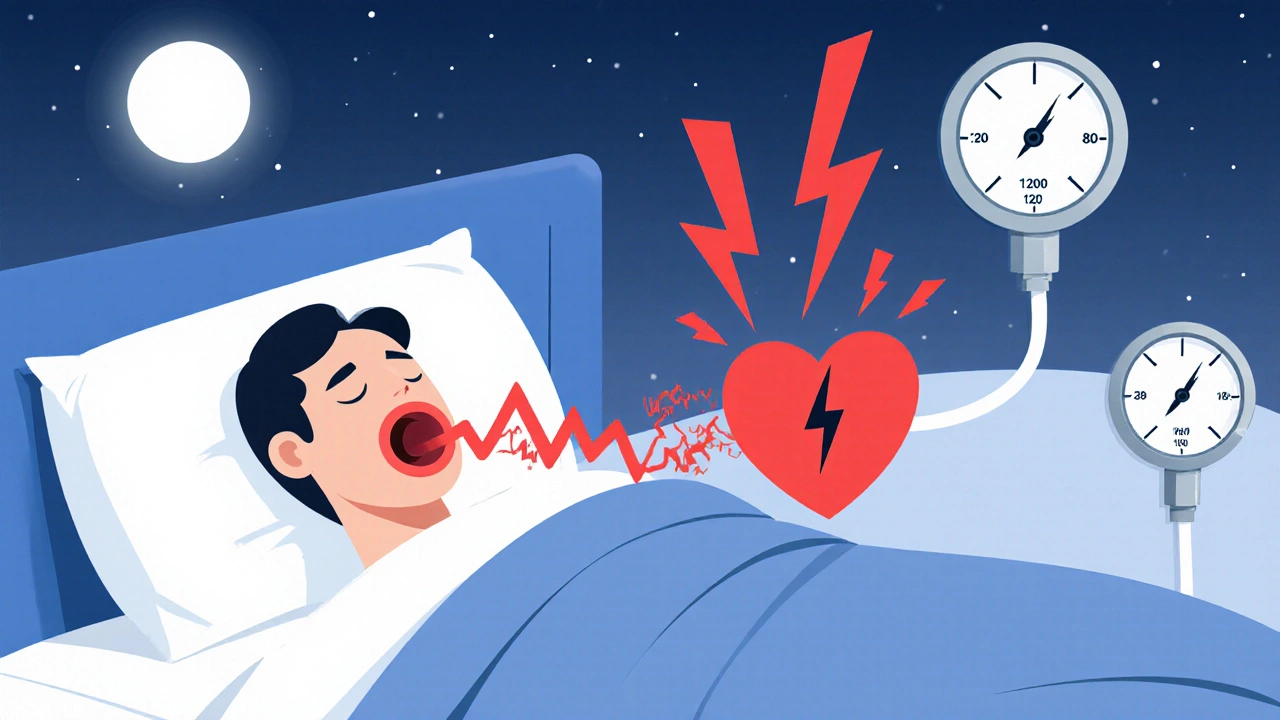

Sleep Apnea and Heart Risk: How Snoring Can Raise Blood Pressure and Trigger Arrhythmias
Sleep apnea isn't just about snoring-it raises blood pressure, triggers dangerous heart rhythms, and increases heart attack and stroke risk. Learn how untreated sleep apnea harms your heart and what actually works to fix it.
View More