Fluid Intake: How Much You Really Need and Why It Matters for Medications and Health
When we talk about fluid intake, the total amount of liquids consumed daily, including water, beverages, and moisture from food. Also known as hydration, it’s not just about quenching thirst—it directly impacts how your body processes medications, manages side effects, and maintains basic functions. Too little can turn a mild drug reaction into a hospital visit. Too much can strain your kidneys or throw off your electrolytes. And most people have no idea where they fall on that spectrum.
Dehydration, a state where your body loses more fluids than it takes in is a silent risk with many meds. Diuretics like hydrochlorothiazide? They pull fluid out—so if you’re not replacing it, you risk dizziness, low blood pressure, or even kidney stress. Opioids cause nausea and constipation—both worsen without enough fluids. Even common drugs like lamotrigine or amitriptyline can affect how your body holds onto water, making you more vulnerable to imbalance. And don’t forget electrolyte balance, the critical mix of sodium, potassium, and other minerals that regulate nerve and muscle function. When fluid intake drops too low, these minerals get out of whack. That’s when you get cramps, irregular heartbeat, or brain fog—even if you’re drinking water.
Fluid intake isn’t one-size-fits-all. A healthy adult might need 2-3 liters a day, but someone on antibiotics for C. difficile needs more to flush out toxins. Someone with heart failure or kidney disease might need to limit it. Your meds, your activity level, your climate, even your age—all change the math. And no, coffee and soda don’t fully count as hydration. They might help, but they also have diuretic effects that can undo the benefit.
What you’ll find below are real stories from people who learned the hard way. How a simple change in fluid intake helped manage opioid nausea. Why dehydration made a thyroid issue worse while on lamotrigine. How drinking too little turned a routine antibiotic into a C. difficile nightmare. These aren’t theories—they’re experiences from real patients, backed by clinical patterns. You’ll see what works, what doesn’t, and what your doctor might not have told you.
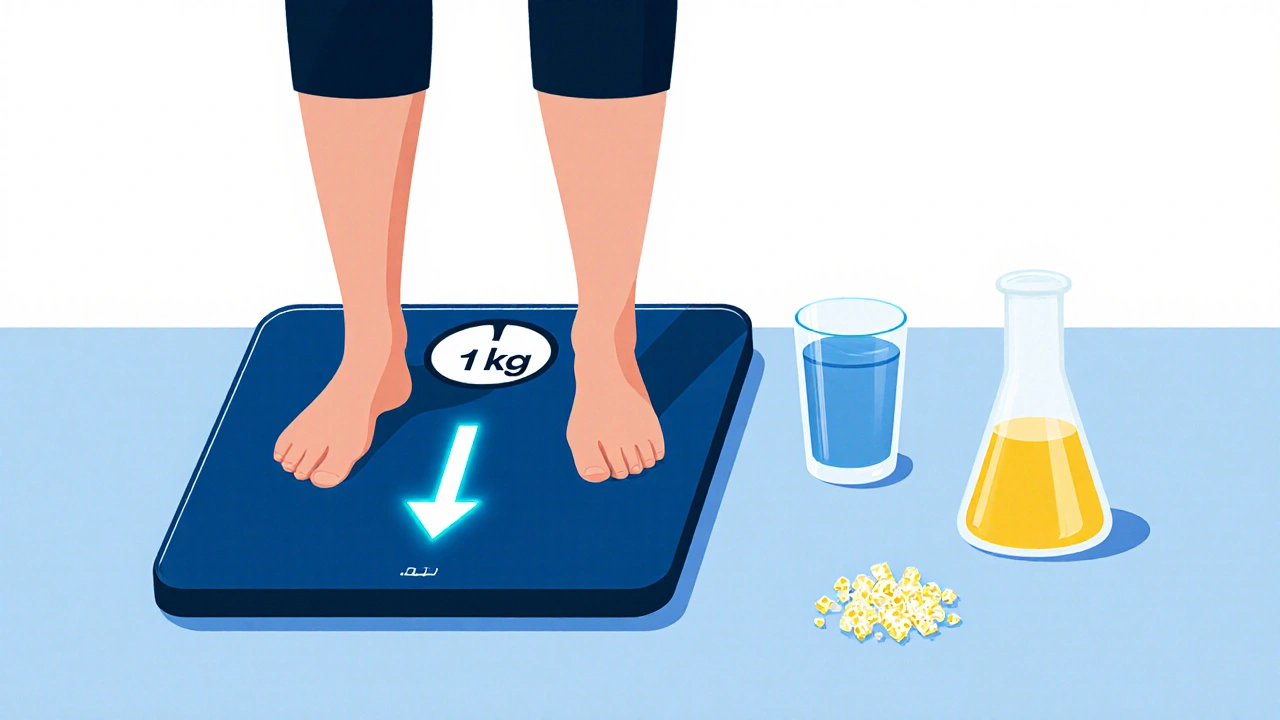

Hydration and Diuretics: How to Balance Fluid Intake to Avoid Side Effects
Learn how to balance fluid intake when taking diuretics to avoid dehydration, electrolyte loss, and dangerous side effects. Practical tips on water, electrolytes, weight tracking, and what to avoid.
View More