PPIs and Antifungals: How They Interact and What You Need to Know
When you take proton pump inhibitors, medications that reduce stomach acid to treat heartburn and ulcers. Also known as PPIs, they're among the most prescribed drugs in the world. But if you're also using antifungals, drugs that kill or slow down fungal infections like yeast or athlete's foot. Common examples include fluconazole, itraconazole, and ketoconazole, things can get tricky. PPIs lower stomach acid—and that acid isn't just there to digest your food. It's also a barrier that helps certain antifungals dissolve and get absorbed. When acid drops too low, some antifungals don't work as well. That means your infection might not clear up, even if you're taking the right medicine.
This isn't just about one drug failing. It's about a chain reaction. Lower acid from PPIs can lead to fungal overgrowth in the gut, which makes antifungal treatment harder. Some antifungals, like itraconazole, need acid to be absorbed properly. If you're on omeprazole or esomeprazole and also taking itraconazole for a persistent fungal infection, you might be fighting the treatment without realizing it. And it's not just absorption. Some antifungals slow down how your liver breaks down other drugs, which can push PPI levels too high and increase side effects like headaches, diarrhea, or even long-term risks like bone loss or kidney issues. These aren't rare edge cases. Studies show up to 1 in 5 people on long-term PPIs also get antifungals—often without anyone checking if they clash.
You might not even know you're at risk. A yeast infection after antibiotics? A rash that won't go away? Your doctor might reach for an antifungal. Meanwhile, your daily heartburn pill is quietly making it harder for that antifungal to do its job. The fix isn't always stopping the PPI—it's timing, switching antifungals, or using alternatives like topical treatments. Some antifungals, like fluconazole, aren't as affected by stomach acid, so they're safer to use with PPIs. But you need to know which ones are which. And if you're on multiple meds, even over-the-counter ones, it's easy to miss these hidden conflicts.
The posts below dive into real-world cases where these interactions matter—from how PPIs mess with antifungal absorption, to why some people get recurring infections despite treatment, to what alternatives actually work without the risk. You'll find guides on spotting the signs of a failed antifungal, how to talk to your pharmacist about drug clashes, and what to ask your doctor before starting a new prescription. No fluff. Just what you need to make sure your meds work the way they should.
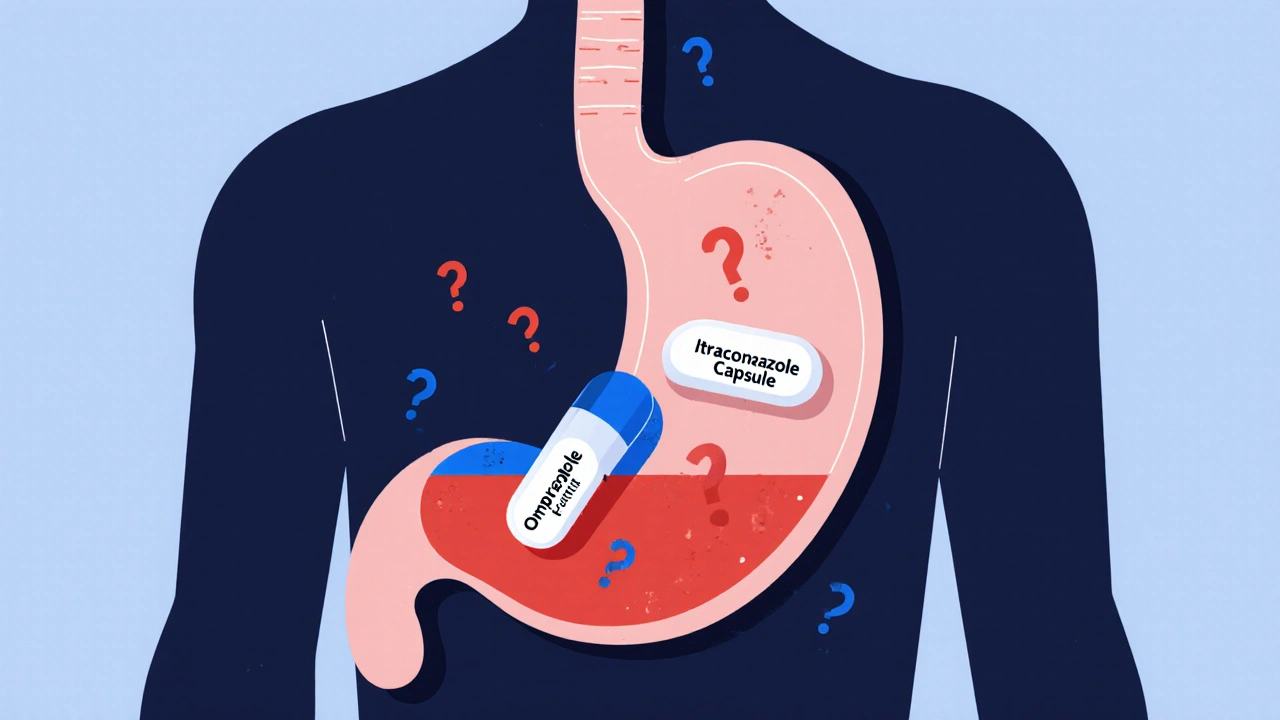
Proton Pump Inhibitors and Antifungals: How They Interfere with Absorption
Proton pump inhibitors can block the absorption of key antifungals like itraconazole, leading to treatment failure. Learn which drugs interact, how to fix it, and what new options are available.
View More




